Vent-Axia has welcomed the raised awareness surrounding the importance of good indoor air quality following the latest findings which reveal the significant risk of polluted indoor air in our homes.
According to a recent survey by trade association BEAMA over one third of UK homes are at an elevated or severe risk of having polluted indoor air. The My Health My Home survey revealed that 35% of respondents potentially had this risk in varying levels of severity.
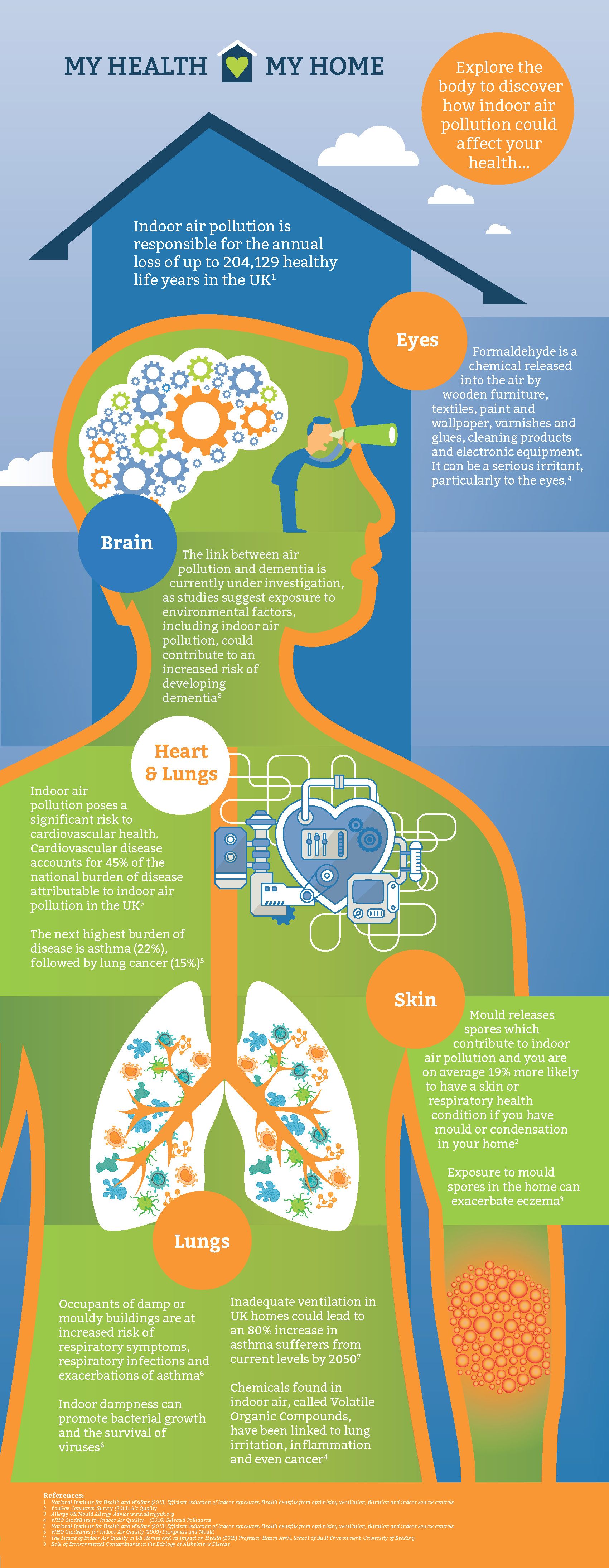
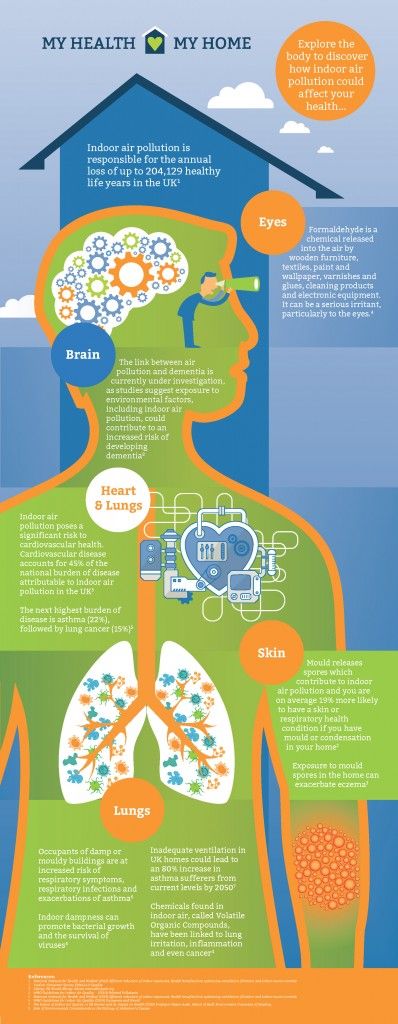
This survey is significant since it highlights the numbers of homes that could be at risk of breathing in polluted air and follows on from the latest research on indoor air quality by a leading academic at The University of Reading. Professor Hazim Awbi’s report, “The Future of Indoor Air Quality in UK Homes and its Impact on Health”, states the health risks associated with poorly ventilated homes in no uncertain terms.
One of the revelations in this new report is that, as new and refurbished homes become ever more air tight to meet the government’s carbon emission targets for 2050, the number of people suffering with asthma could almost double by then. It also states that current building regulations could increase indoor pollutant levels quivalent to the upper end of (and in some cases well above) World Health Organisation (WHO) recommended limits.
The report examines how increasing levels of energy efficiency will impact on pollution levels and health if there is no additional intervention, over and above existing requirements. Key projections for 2050 include: an 80% increase in asthma sufferers from current levels; Total volatile organic compound concentrations up to 60% above WHO 24 hour limits; and nitrogen dioxide concentrations up to 30% above WHO annual limits.
‘‘To avoid a serious and significant increase in asthma cases, which could be up to 80%, and other health conditions related to poor indoor air quality, homes must be adequately ventilated. In addition to the need for mechanical ventilation systems I would also advise that a minimum air exchange rate that new homes must meet is enforced and there is tighter regulation to ensure systems are adequately installed, operated and maintained,’’ said professor Awbi.
In addition, the report suggests that there should be a legal requirement for new homes, and guidance for retrofitted homes, to have an air exchange rate of at least 0.5/hour, to help protect human health. It states that the most cost-effective solution for achieving this exchange rate, while still satisfying energy efficiency requirements, is the standardised fitting of effective continuous mechanical ventilation, preferably with heat recovery.
“At Vent-Axia we welcome this new research which confirms there is no doubt that poor indoor air quality has an adverse impact on health. It is important that the public is aware of the dangers of poorly ventilated homes,”
